布尔类型
hello,我们又见面了,在开始今天的内容之前,我们来看一点点有趣的东西——布尔类型(bool)。
定义的方法: bool 变量名=真(true)或假(false);
比如说:bool flag=true;,定义布尔变量时,不给默认值则该变量为假。
我们也可以直接把布尔类型的变量定义为表达式,它会自动运算结果,并决定变量的值的真假。
例如:bool flag=(100>99);,这里的变量的值为真;重新定义flag=(100<99);,这时变量的值为假。
需要注意的是:
- 除了0以外的其他任何数字的布尔值为真,只有0为假。同样的,空字符常量的布尔值为0。
- 任何逻辑表达式的结果都可以归结为真或假,即布尔类型的变量。
- 当你想要给一个布尔类型的变量取反值时,你可以巧妙地使用取反符,比如这样:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
bool s=false;
s=!s;
cout<<s;
return 0;
}
或者这样:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
bool s=false;
s=not s;
cout<<s;
return 0;
}
判断
判断,想必大家都不陌生。在大多数语言里面,判断用的语句叫 if 语句,Python与C++也有许多相似之处。
例如,在python里,if是这么写的:
if something:
# put your code here
pass
elif something:
# put your code here
pass
else:
# put your code here
pass
而C++要这么写:
if(something){
// your code
;
}
else if(something){
// your code
;
}
else{
// your code
;
}
当if语句小括号内的布尔值为真的话,就会执行对应大括号内的指令,即程序中something的
C++与Python的逻辑运算符也有些许不同,如下表:
| Python | C++ | 语义 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|---|
and |
&& |
逻辑与 | 一假则假 |
or |
|| |
逻辑或 | 一真则真 |
not |
not |
取反 | 真假互换 |
在目前的阶段,我们只会在逻辑表达式中使用这些逻辑运算符,在非布尔值的表达式中运用这些符号,不会得到布尔类型的值。
两种语言中逻辑运算符的用法差不太多,例如python中a and b,在C++里边表示为a&&b。
现在我们再来说说判断运算符:
| Python | C++ | 语义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|---|
== |
== |
等于() | 100==100 返回真;100==99 返回假 |
!= |
!= |
不等于() | 123!=345 返回真;123!=123 返回假 |
< |
< |
小于() | 1<2 返回真;1<0 返回假 |
> |
> |
大于() | 3>2 返回真;3>4 返回假 |
<= |
<= |
小于等于() | 1<=1 返回真;2<=1 返回假 |
>= |
>= |
大于等于() | 1>=0 返回真;1>=2 返回假 |
一起来试试吧:
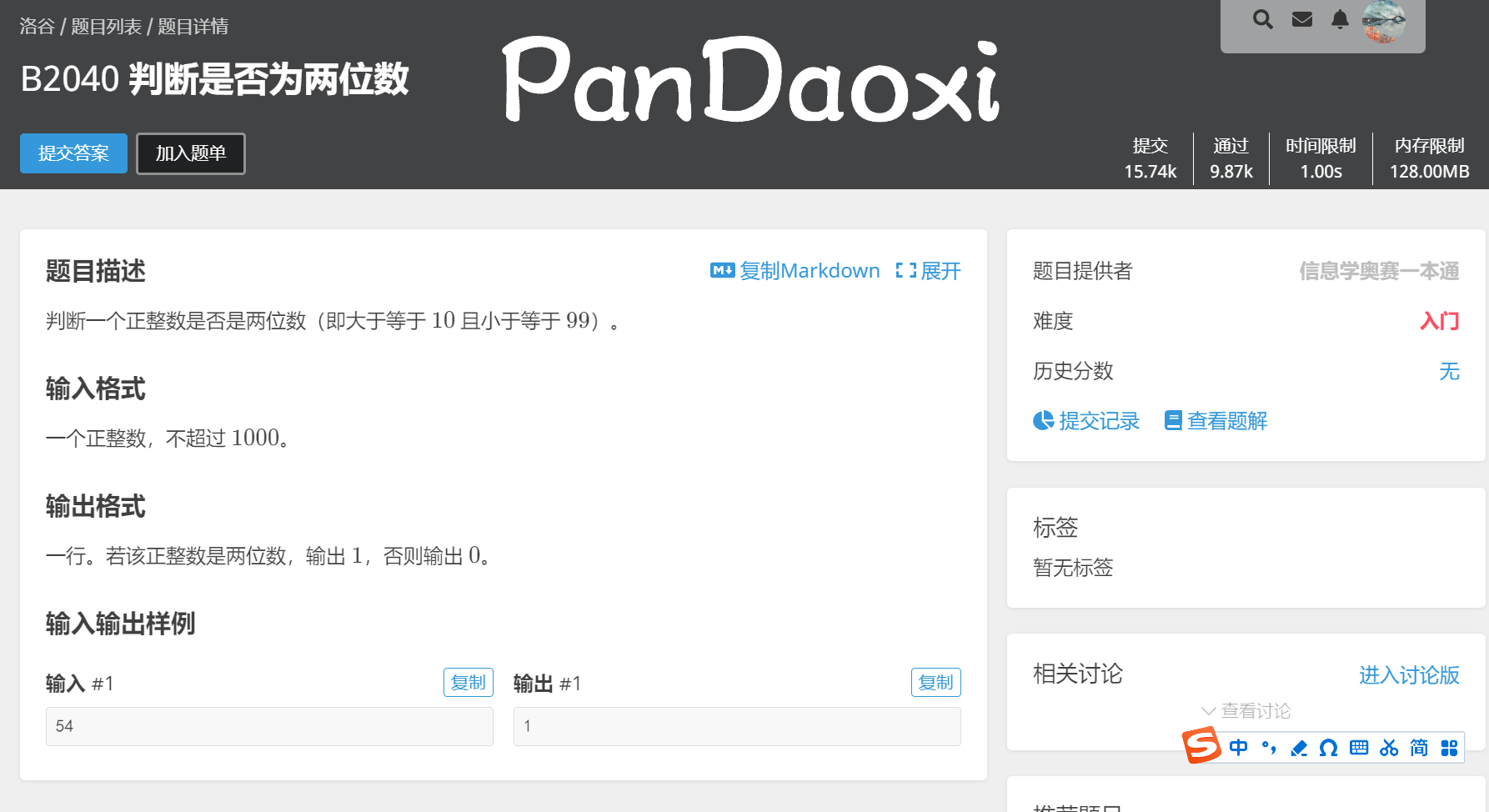
显而易见,我们只需要用一个if和一个else就可以了~
如果你的代码是这样的,就说明你已经掌握了一部分的判断语句😁
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
// if后只有一句可以不用加大括号。
if(n>=10&&n<=99) cout<<1;
else cout<<0;
return 0;
}
当然,我们可以妙用除法:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
if(n/10>=1&&n/10<=9) cout<<1;
else cout<<0;
return 0;
}
既然这题没啥问题了,就再来一题吧!😄
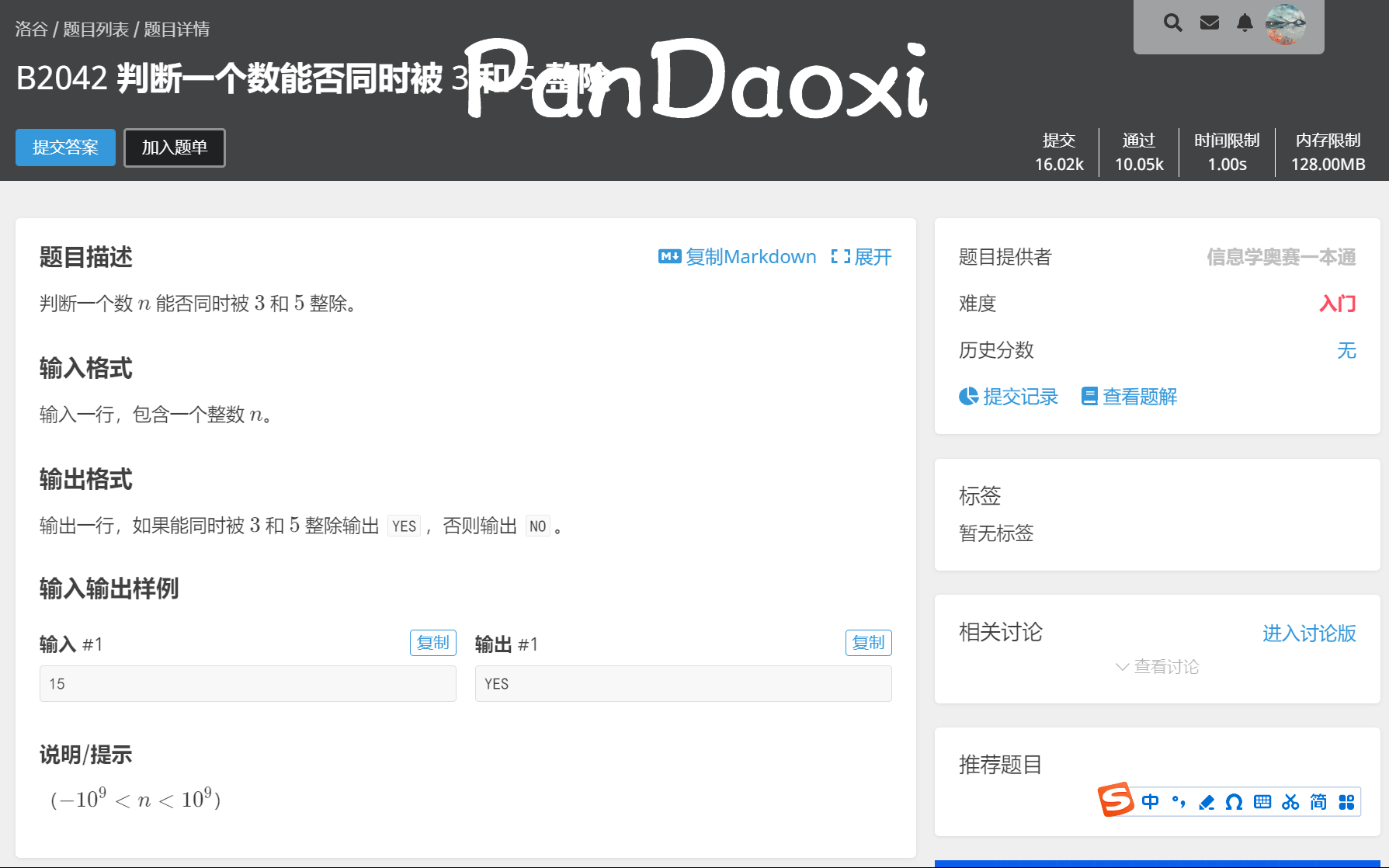
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
// 对15取余为0 相当于 被15整除
if(n%15==0) cout<<"YES";
else cout<<"NO";
return 0;
}
哇,你好厉害啊!现在,我们来继续增大难度,看一个有趣的东西——三目运算符。
三目运算符
三目运算符的基本结构是:
(表达式或布尔值) ? 真值要做的事 : 假值要做的事
例如:(a>b)?b=a:a=b,给出整数 和 ,那么请问这是在干嘛呢?
表达式的意思是在说: 如果 成立,就把 的值赋给 ;反之就把 的值给 。
如何利用三目运算符比较三个数中最大的呢?
((a>b)?((a>c)?a:((b>c)?b:c)):((b>c)?b:c))
看起来很麻烦的样子,我们来仔细理解一下😅。
先比较 a 和 b 的大小,如果 b 大,就用 c 和 b 作比较,如果 b 大,b 就是最大的那个;如果最开始 a 大,就用 a 和 c 作比较,如果 a 大, a 就是最大的,如果 c 大,那再拿 b 和 c 作比较,拿到最大的。
好家伙,这么麻烦啊??

不过好在,我们有函数来帮忙。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
// cout<<((a>b)?((a>c)?a:((b>c)?b:c)):((b>c)?b:c));
cout<<max(max(a,b),c);
return 0;
}
好啦好啦,接下来我们来放松一下,来看看循环……
三种循环
在讲循环以前,我们要先来学一点点操作符号,方便大家理解!

这方面Python和C++的差别并不太大,你看:
(假设我们有一个整数类型的变量 )
| Python | C++ | 含义 | 运行结果 | 返回值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
a+=1 |
a++ |
a的值增加1 | 11 | a |
a-=1 |
a-- |
a的值减少1 | 9 | a |
a+=1 |
++a |
a的值增加1 | 11 | a+1 |
a-=1 |
--a |
a的值减少1 | 9 | a-1 |
a+=10 |
a+=10 |
a的值增加10 | 20 | a+10 |
a-=10 |
a-=10 |
a的值减少10 | 0 | a-10 |
a*=5 |
a*=5 |
a的值乘5 | 50 | a*5 |
a/=5 |
a/=5 |
a的值除以5 | 2 | a/5 |
a%=3 |
a%=3 |
a的值对三取余 | 1 | a%3 |
当然不排除,大家是不是见过a++和++a?有何区别?
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=10;
cout<<(a++)<<endl;
a=10;
cout<<(++a)<<endl;
return 0;
}
可见输出的结果为:10 11。
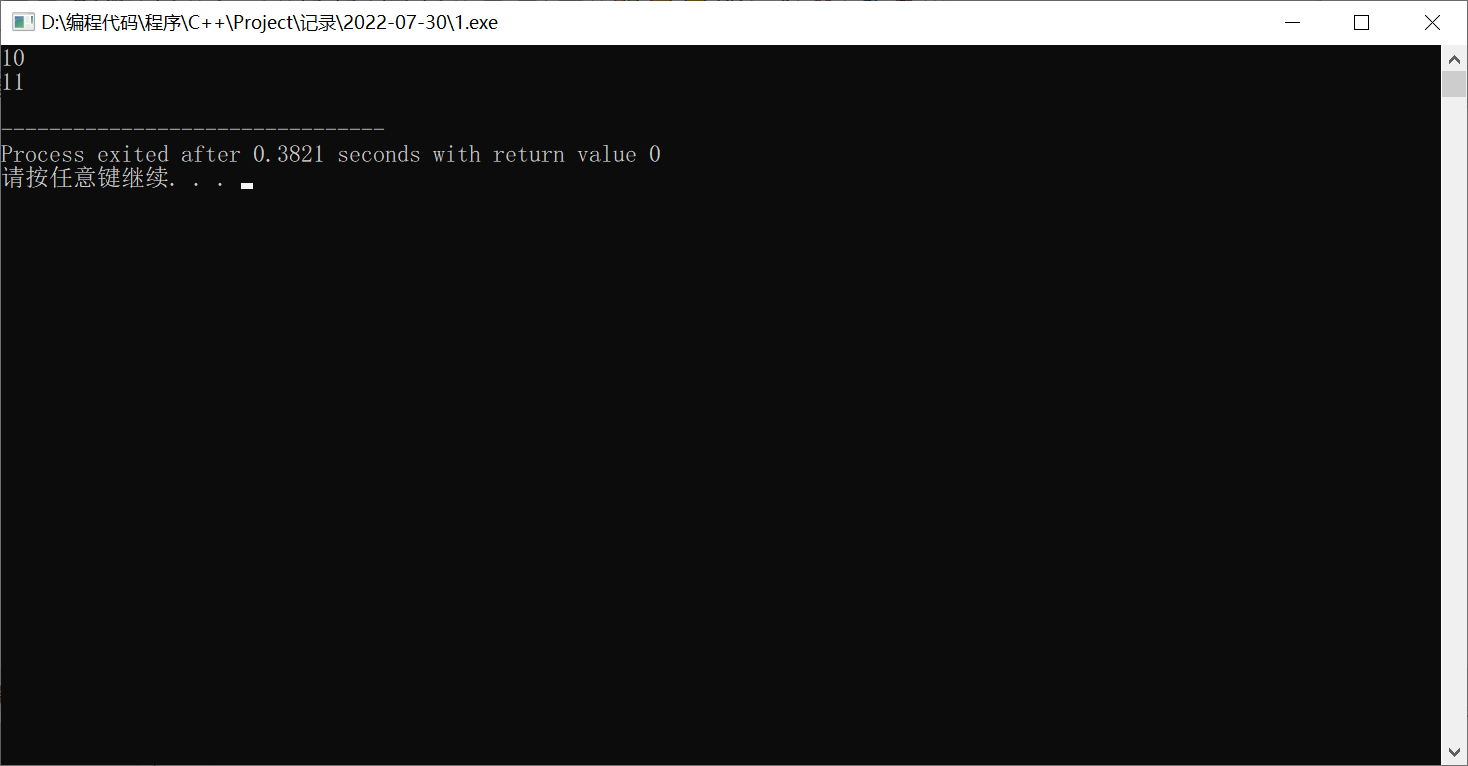
a++为先输出、再加,但是因为下面重新给a赋值为10,所以看不到效果;但是重新赋值以前 a 的值已经是11了。
++a为先加再输出。
现在,我们来看看第一种循环:while循环。
while 循环
while循环,我们在python里经常见吧?!
格式是差不多的:
while(表达式或布尔类型的值){
你要执行的指令
}
当表达式的值为假时,循环停止,继续运行下面的指令。
但如果你写成了 while(true) (死循环),就会一直跑,跑啊跑,至死方休。
看一个简单的小例子,输出1~100的数:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=1; // 给定初始值为1
while(index<=100){ // 当 index=101 时,不满足条件,就退出了
cout<<index++<<" "; // 先输出,再增加
}
cout<<endl<<endl<<"继续执行后面的指令。"<<endl;
cout<<"循环过后 index="<<index;
return 0;
}
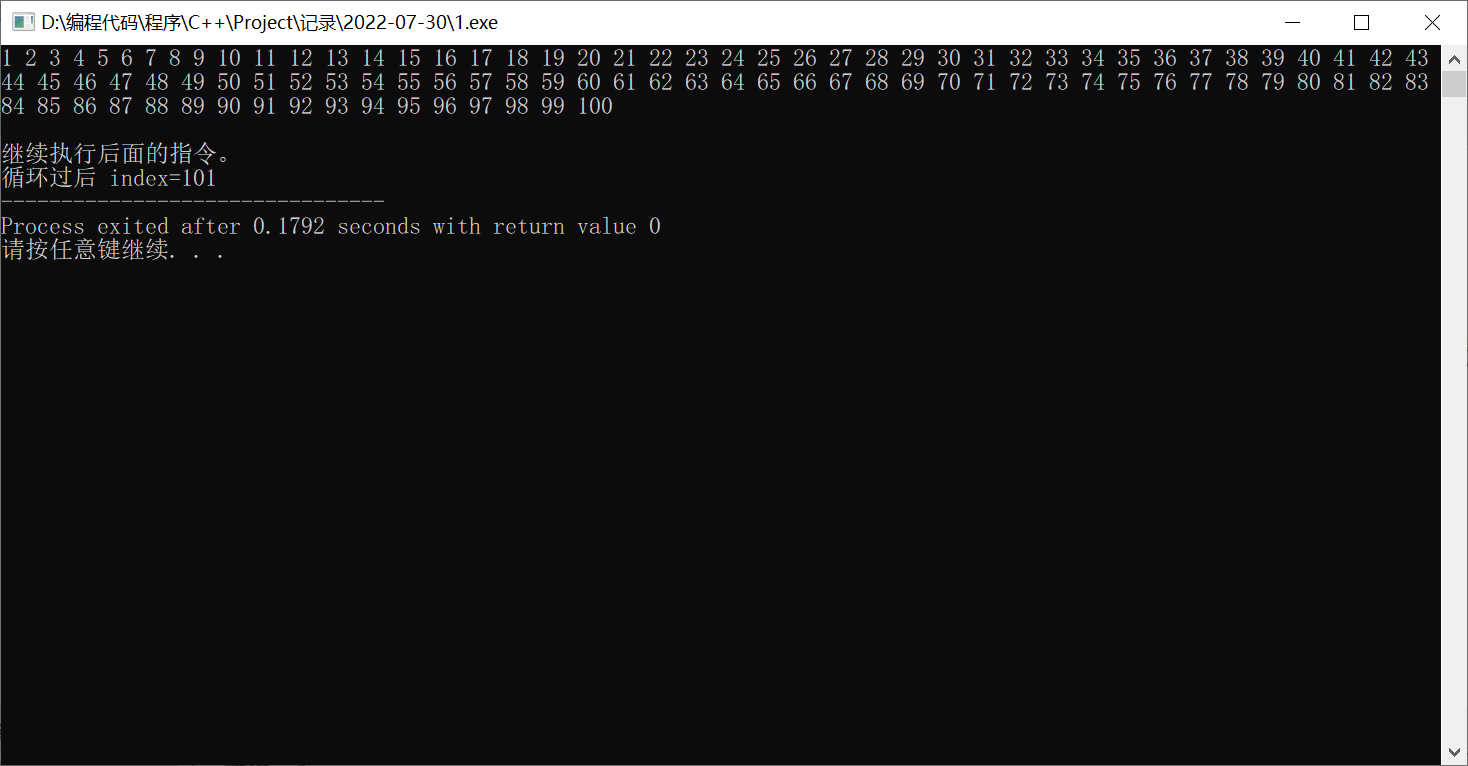
可以看到,循环过后的指令也被执行了。当index的值超过100后,循环就不满足条件,继续执行循环过后的指令了。
continue
那么,我们想,如何跳过50继续循环呢?
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=0;
while(index<100){
// 要先增加,然后在判断是否为50,这样既保证了index增加,又确保能够跳过50。
if((++index)==50) continue; // 遇到50就跳过,继续循环
cout<<index<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
继续看,如果我们想要跳过3的倍数呢?
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=1;
while(index<=100){
if(index++%3==0) continue;
cout<<index-1<<" "; // 因为过早地加上了,还需要减掉1
}
return 0;
}
那么请你来分析一下这个程序的错误原因吧:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=1;
while(index<=100){
if(index%5==0) continue; // 跳过5的倍数
cout<<index<<" ";
index++;
}
return 0;
}
程序为什么只输出了 1 2 3 4 然后就不动了?
答:我们在考虑问题时一定要周全,当第四次循环完成,这时 index=5,第五次循环刚刚开始遇到 continue 语句,跳了过去;第六次循环,index没有增加,所以index的值还是5,遇到 continue 跳了过去,形成了死循环。
如何修改?只需要让跳过的时候,index的值也增加1。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=1;
while(index<=100){
if(index%5==0) index++;
cout<<index<<" ";
index++;
}
return 0;
}
break
break,打破循环。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=1;
while(index<=100){
// 当index的值为50时,终止循环。
if(index==50) break;
cout<<index++<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
所以只输出到49,程序就结束了。
break语句比较简单,还有一个switch语句也用break,但是用得不多,比if繁琐得多,我就不多说了。
do-while循环
这个循环和while其实很像,但是有一点一定要注意:不管while内是真是假,do内的指令都会执行。
例如:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
do{
cout<<"hi";
}while(false);
return 0;
}
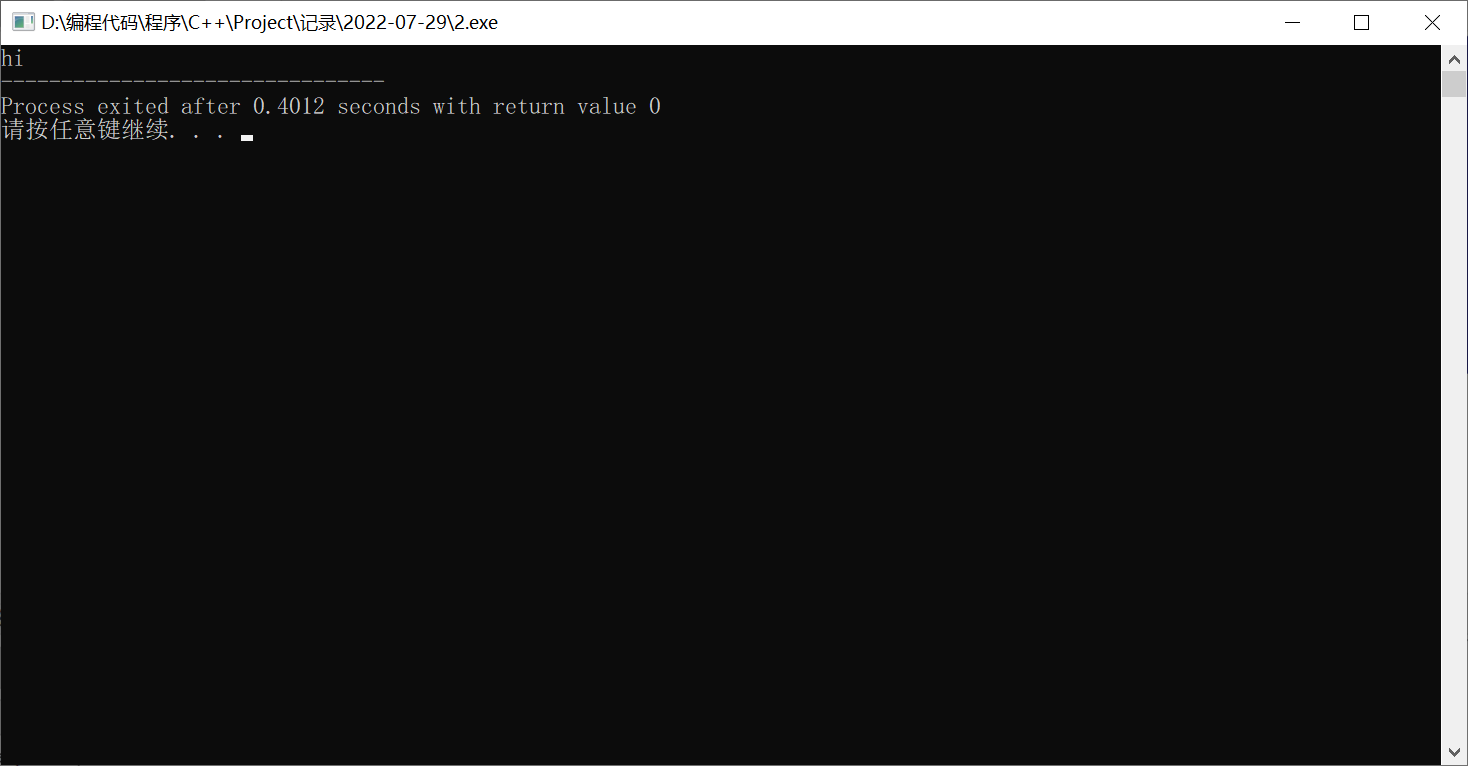
可以这样输出1~100:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int index=1;
do{
cout<<index++<<" ";
} while(index<=100);
return 0;
}
for循环
for循环是重中之重。
你看一个比较高级的算法里,很少有不带for的:

咳咳咳扯远了,我们还是先看看怎么用吧。
for(int 循环内变量=初始值;循环逻辑表达式;变量的变化){
要执行的指令
}
有没有觉得很复杂?其实你看,很简单的:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){
cout<<i<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
我最开始也不喜欢用for,但是慢慢就发现还是for最省力气。
来练练手:
请使用for循环输出N个正整数(小于100)的最大值。
输入:
5
1 2 5 4 3
输出:
5
这时候,我们使用一种不一样的办法。这种办法本质上我觉得像是一种递推算法,推出来最大的数。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,tmp,maxn=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
// 输入这个数
cin>>tmp;
if(tmp>maxn){
// 如果比当前最大的还大,就让它成为最大的
maxn=tmp;
}
}
cout<<maxn;
return 0;
}
呀哈没考住你,再来一道!
请使用for循环输出N个正整数(小于100)的最大值、最小值、平均值。
输入:
5
2 3 1 4 5
输出:
5 1 3
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,minn=0xcffff,maxn=0,avgn=0;
int tmp; // 临时变量
cin>>n;
// 循环,输入
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>tmp;
// 更新最大值
maxn=max(maxn,tmp);
// 更新最小值
minn=min(minn,tmp);
// 计算和
avgn+=tmp;
}
// 输出
cout<<maxn<<" "<<minn<<" "<<avgn/n;
return 0;
}
好啦,今天就先到这里吧,明天再见咯~