分享笑话一则:我翻到了以前我写的程序,在洛谷上存着:
大概是我自己弄了半天然后 了,这么激动。
栈这个东西,大家肯定都听说过,那咱们再跳过一次?
不管怎么样,我们还得再说说。
栈
我们的 有一个大杀器—— 模板库。
我们可以使用万能头文件,然后用下面这行代码创建一个栈:
// 创建一个整数类型的栈 s
stack <int> s;
创建这个栈以后,我们先看一个神奇的东西——结构体。
结构体
结构体允许用户创建自己的数据类型,方便使用。我们可以用 创建结构体。
// main 外
struct hhh{
// 变量,各种类型
int a;
char b;
bool c;
long long d;
double e;
int f[114];
short g[514];
string h;
// 函数
void read(){
cin >> a >> b;
}
// 其他各种内容都可以塞进来
}; // 注意有分号!
// 创建一个hhh类型的数组
hhh qwp[11];
// 创建一个hhh类型的变量
hhh abc;
int main(){
abc.read();
for(int i=1; i<=10; i++) qwp[i].read();
// ...
return 0;
}
结构体数组支持 函数排序。
/*
用法:
sort(数组名+起始下标, 数组名+终止下标, 自定义的排序函数);
*/
struct ha{
int a, b;
}
bool cmp(ha x, ha y){
// 返回 x 大于 y 的情况
if(x.a != y.a) return x.a > y.a;
else return x.b > y.b;
}
int main(){
ha a[5];
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){
cin >> a[i].a >> a[i].b;
}
sort(a+1, a+6, cmp); // 其实那玩意儿叫地址,但是太麻烦了,我们后面再说
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++){
cout << a[i].a << " " << a[i].b;
}
}

提高组考这大水题有点儿过分了啊
我们来一起看看这个题,这是我初学的时候写的程序:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct stu {
string name="";
int s1=0, s2=0, s3=0, total=0;
char t1=0, t2=0;
void work() {
if(s1 > 80 && s3 > 0) total += 8000;
if(s1 > 85 && s2 > 80) total += 4000;
if(s1 > 90) total += 2000;
if(s1 > 85 && t2 == 'Y') total += 1000;
if(s2 > 80 && t1 == 'Y') total += 850;
}
} s[101]; // 简略写法,表示直接创建一个数组
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) cin >> s[i].name >> s[i].s1 >> s[i].s2 >> s[i].t1 >> s[i].t2 >> s[i].s3;
string name = "";
int tot1=0, tot2=0;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
s[i].work();
tot2 += s[i].total;
if(s[i].total > tot1) tot1 = s[i].total, name = s[i].name;
}
cout << name << endl << tot1 << endl << tot2;
return 0;
}
模拟栈
栈是一种线性数据结构,你也可以想成就是一条很窄的路,元素只能一个一个过。
如果这条路的一头“咔”,堵死了,那这就是一个栈。
你看,就是这样的:
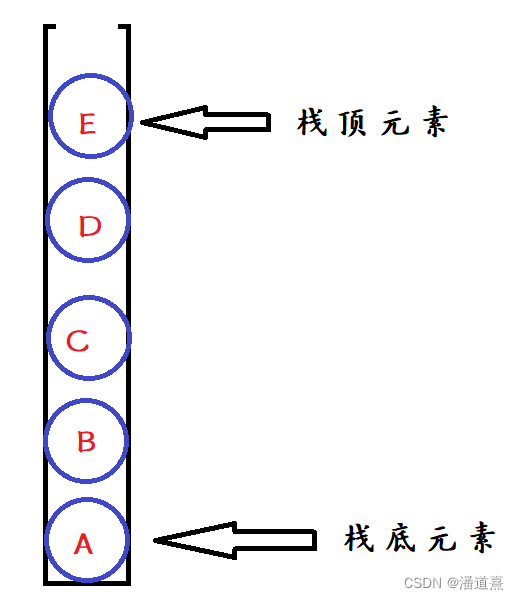
那么,我要弹出一个元素,肯定是要先弹出栈顶咯。这也是一个栈的基本概念:先进后出。
“噗”,元素 出去了,栈顶变成了 。
,咱们可爱的小电脑怎么知道这个操作呢?
——我们需要一个指针 (其实也就是变量,不是那种指针),指向栈顶元素的下标,弹出时这个指针自减;进入时,这个指针自增;如果按照这个思路,那么栈中一共有 个元素。
按照上面的思路,我们可以写出栈的模拟:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int inf = 114514;
struct stack_int{
// 栈顶指针、模拟数组
int t = 0,
st[inf];
// 函数
void push(int k){ // 压入栈顶
st[t++] = k;
}
void pop(){ // 踢出栈顶
st[t--] = 0;
}
bool empty(){ // 判空
return t <= 0;
}
int size(){
return t;
}
int top(){
if(!empty()) return st[t-1];
else return INT_MAX; // 传回一个错误值
}
};
int main(){
stack_int st; // 创建一个栈
st.push(191); // 压入114
st.push(9810); // 压入9810
st.push(114514); // 压入114514
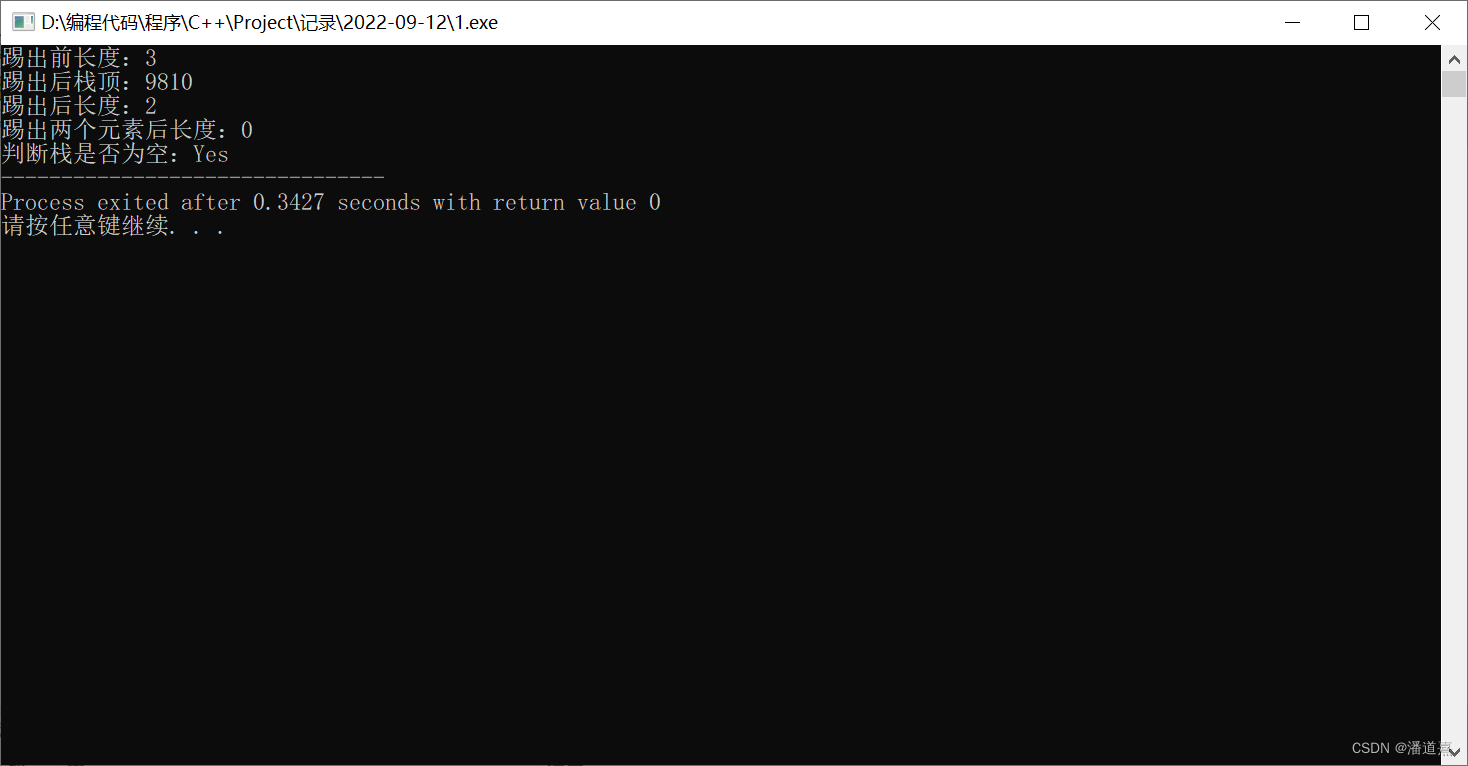
printf("踢出前长度:%d\n", st.size());
st.pop();
printf("踢出后栈顶:%d\n", st.top());
printf("踢出后长度:%d\n", st.size());
st.pop();
st.pop();
printf("踢出两个元素后长度:%d\n", st.size());
printf("判断栈是否为空:%s", (st.empty() ? "Yes" : "No"));
return 0;
}
大杀器
我们可以使用模板库简化刚才的例子。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack <int> st; // 创建一个栈
int main(){
st.push(191); // 压入114
st.push(9810); // 压入9810
st.push(114514); // 压入114514
printf("踢出前长度:%d\n", st.size());
st.pop();
printf("踢出后栈顶:%d\n", st.top());
printf("踢出后长度:%d\n", st.size());
st.pop();
st.pop();
printf("踢出两个元素后长度:%d\n", st.size());
printf("判断栈是否为空:%s", (st.empty() ? "Yes" : "No"));
return 0;
}
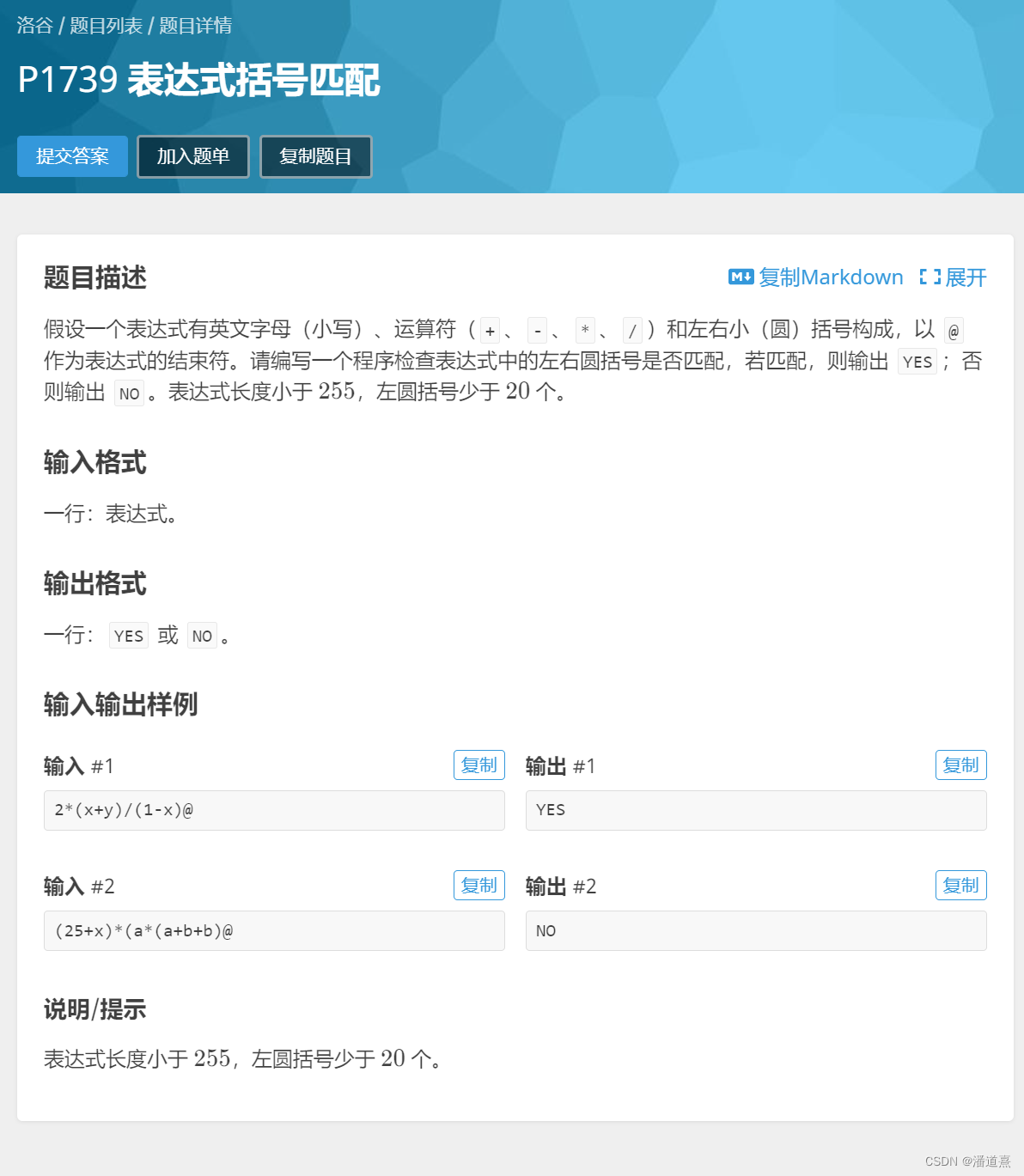
练习
其实这个题直接暴力模拟也是可以的。我初学 那会儿写的程序也没用栈:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string x;
int a = 0;
cin >> x;
for(int i=0; i<x.size(); i++){
if(x[i] == '(') a++;
if(x[i] == ')') a--;
if(a < 0){
cout << "NO";
return 0;
}
}
cout << (a ? "NO" : "YES");
return 0;
}
下面放出标准答案:
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack <char> st;
int main(){
char c;
while(cin >> c){
if(c == '@') break;
if(st.empty() && c == ')'){ // 特判
cout << "NO";
return 0;
}
if(c == '(') st.push(c);
if(c == ')') st.pop();
}
cout << (st.empty() ? "YES" : "NO");
return 0;
}

这真的是老师讲的例题!直接模拟,胆大心细就行。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<unsigned long long> st;
int main(){
int T;
cin >> T;
for(int j=0; j<T; j++){
unsigned long long n, m;
string s;
cin >> n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
cin >> s;
if(s == "push"){
cin >> m;
st.push(m);
}
else if(s == "pop"){
if(st.empty()) cout << "Empty" << endl;
else st.pop();
}
else if(s == "size") cout << st.size() << endl;
else if(s == "query"){
if(st.empty()) cout << "Anguei!" << endl;
else cout << st.top() << endl;
}
}
while(!st.empty()) st.pop();
}
return 0;
}
先说最简单的模拟思路,我们输入一个字符串,从头开始遍历。
如果当前字符为数字,往临时字符串里储存。
如果遇到点,把字符串整成数往栈里存。
如果是符号,拿出来栈顶的两个元素计算结果(那两个元素 掉),然后再 进栈。
最后输出栈顶。
// Author:PanDaoxi
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack <int> st;
int sti(string s){
int n = 0;
for(int i=0; i<s.size(); i++){
n = 10*n + (s[i]-'0');
}
return n;
}
int main(){
string s, temp="";
cin >> s;
for(int i=0; i<s.size(); i++){
if(s[i] == '@') break;
if('0' <= s[i] && s[i] <= '9'){
temp += s[i];
}
if(s[i] == '.'){
st.push(sti(temp));
temp = "";
}
if(s[i] == '+'){
int x = st.top();
st.pop();
int y = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(x + y);
}
else if(s[i] == '-'){
int x = st.top();
st.pop();
int y = st.top();
st.pop();
// 前面的减后面的
st.push(y - x);
}
else if(s[i] == '*'){
int x = st.top();
st.pop();
int y = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(x * y);
}
else if(s[i] == '/'){
int x = st.top();
st.pop();
int y = st.top();
st.pop();
st.push(y / x);
}
}
cout << st.top();
return 0;
}
